library(foreign)
db <- read.spss(file=paste0(getwd(),
"/data/1186_Selects2019_CandidateSurvey_Data_v1.1.0.sav"),
use.value.labels = T,
to.data.frame = T)
sel <- db |>
dplyr::select(B11,B6,T9a) |>
stats::na.omit() |>
dplyr::rename("consultant"="B11",
"personalization"="B6",
"party_list"="T9a") |>
plyr::mutate(party_list=as.factor(party_list))Logistic regression presentation
Learn what logistic regression is and how to run the analysis in R
1 Logistic regression
1.1 Definition and application
The reliance on logistic models can be useful to answer research questions such as:
- modelling the probability of an event that depends other variables: e.g., what is the probability that a candidate with a budget of 10,000 CHF hires a political consultant?
- predicting the association (effect) of several variables on an event: e.g., is the campaign budget a good predictor of hiring a political consultant?
1.2 Binary dependent variable
Logistic regression is a model with a binary dependent variable (e.g., 0 = not elected versus 1 = elected). In this case, we are interested in knowing the probability of a phenomenon (e.g., get elected, lose a job, becoming sick, etc) to occur:
\[Y(P=1)=a+bX+e\] also referred as Linear Probability Model (LPM).
- \(Y(P = 1)\): probability that the dependent variable Y takes the value 1
- \(a\): intercept (baseline log-odds when X = 0)
- \(b\): regression coefficient (how much the log-odds of Y=1 change with a one-unit increase in X).
- \(X\): independent variable (predictor)
- \(e\): error term (captures unexplained variation)
1.3 Interpretation with LPM
For instance, an increase in political experience (e.g., number of years a candidate has joined his party) by 1 year increases/decreases the probability of being elected as a national representative by \(b*100\) percentage points.
However, the interpretation is complicated be that fact that applying LPM may return values outside the [0,1] interval (probabilities are necessary between 0 and 1!).
LPM poses several issues:
- non-linearity
- non-normal distribution of the errors (only two possible outcomes)
- heteroscedasticity
- difficulty in interpreting the results
Therefore, we need a non-linear model predicting probability of an event which remains in [0,1] bounds. The question is how to constrain all possible outcomes between 0 and 1.
1.4 Non-linear probability models in social sciences
Non-linear probability models are essential in social sciences which often deal with categorical dependent variables (e.g., binary, ordinal, nominal). There exists several models depending of the measurement level of the dependent variable:
- Binomial: binary variable
- Multinomial: categorical variable
- Gaussian: interval variable
- Poisson: count data (discrete)
- Gamma: >0 (non-discrete)
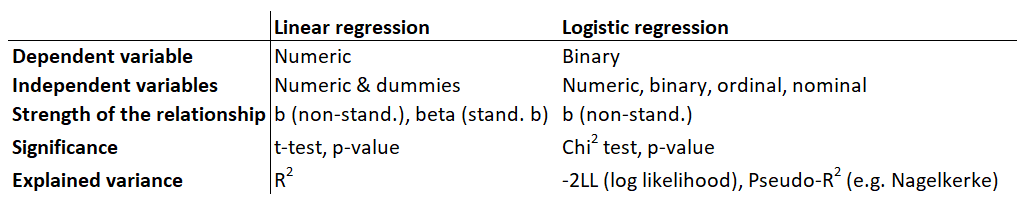
1.5 Differences between linear and logistic regressions
2 Steps in logistic regression
2.1 Three main steps
\(Y\) must be transformed into \(p/(1-p)\) so that the binary dependent variable can be expressed as a function of continuous positive values ranging from 0 to \(+\infty\).
There are usually three steps which are useful to interpret the results from logistic regression:
- p to odds
- odds to log odds
- probabilities
2.2 Step 1: p to odds
Interpretation: “a unit increase in X changes the odds that Y=1 instead of Y=0 by a factor of \(e^z\) (antilog of the odds), all else equal”.
- OR less than 1= negative effect (log-odds)
- OR greater than 1= positive effect (log-odds)
OR give no indication about the magnitude of the implied change in the probabilities.
Let’s look at the following example of two societies:
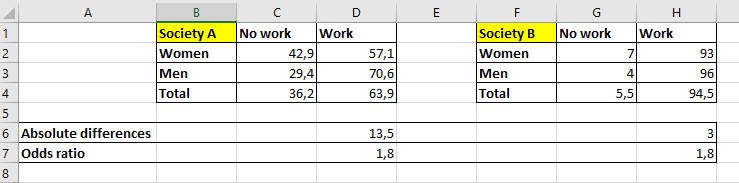
Different differences in probabilities can be associated to the same odds ratio. The social mechanisms responsible for gender effect on having work are the same in the two societies, but the intensity of the effect resulting from those mechanisms is much stronger in A than B.
2.3 Step 2: odds to log odds
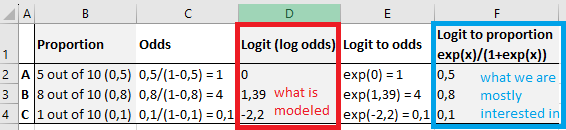
Up to now, we have \(odds=p/(1-p)\), which we now transform into log odds: \(ln(p/(1-p))\).
- If p=0.5, odds=1 and log odds: 0, which suggests no effect
- If p=0.8 of success (0.2 of failure), odds=4 and log odds: 1.38, which suggests a positive effect
- If p=0.8 of failure (0.2 of success), odds=1/4 and log odds: -1.38, which suggests a negative effect
Note: only the sign of the log odds (direction of the coefficient) can be interpreted.
2.4 Step 3: back to probabilities
The problem with log odds (also called logit) is that they are not easy to interpret
Example: “logarithmic odds of an increase in budget by one franc on being elected”.
Therefore, we need to transform log odds into probabilities:
\[P_i(y=1)=\frac{e^{a+b_1x_1+b_2x_2}}{1+e^{a+b_1x_1+b_2x_2}}\]
2.5 Recap
The table below summarized the different measures that are useful for interpreting logistic regression outputs:
3 Model equations and quality
3.1 Equations are very similar to liner regression
The logit of the dependent variable (Y) is estimated by the following equation:
\[ logit(Y) = \beta_0 + \beta_1X_1 + \beta_2X_2 + ... + \epsilon \] The logit does not indicate the probability that an event occurs. To know this probability (prob(Y=1)), it is necessary to apply the following transformation:
\[ proba = \frac{exp^{logit}}{1+exp^{logit}} \]
3.2 Marginal predictions
The main benefit of marginal predictions is that it leaves everything at the mean, except for the variable that you are interested in.
- Continuous covariate: the margins compute how P(Y=1) changes as X changes from 0 to 1, controlling for other variables in the model.
- Dichotomous covariate the marginal effect equates the difference in the adjusted predictions for two groups (e.g., for women and men).
- Discrete covariate: the margins compute the effect of a discrete change of the covariate (discrete change effects).
3.3 Model fit: \(R^2\)
\(R^2\) in OLS is a measure for model fit. It is based on differences between real observations and the regression line. It tries to remove as much error as possible.
In logistic regression, there is no comparable measure since all values on Y are either 1 or 0. We are explaining probabilities (not explained variance).
Note: Pseudo \(R^2=(-2LL0 - -2LL1)/-2LL0\) has no clear interpretation, but provides a good way to compare models (rather than assessing fit).
3.4 Model fit: MLE
The model fit is based on Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) which tries to guess parameters that have highest likelihood of producing observed sample patterns. Likelihood is the probability that our statistical model is actually found in a sample, thus the better the model fits the data, the more likelier it is.
The smaller the Log likelihood the better the model fit: by how much Log likelihood has decreased by adding (a) variable(s), and by calculating the significance of this difference. It is possible to compare models statistically by a Chi-squared test.
Note: Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) are alternative measures (the smaller AIC or BIC, the better the model fit).
4 Empirical example in R
4.1 Example
We would like to predict the likelihood of candidates’ hiring a consultant explained by their campaigning style (e.g., personalization) and their political affiliation.
First, we can load the dataset and select the needed variables:
4.2 Recoding
Then, we can assign the correct levels to the variables and create a personalization score:
# party affiliation
sel$party_list <- gsub(" -.*","",sel$party_list)
sel$party_list <- as.factor(sel$party_list)
sel <- sel[sel$party_list!="No party",]
# consultant
sel$consultant <- ifelse(sel$consultant=="yes",1,0)
sel$consultant <- as.factor(sel$consultant)
# personalization score
sel$personalization <- dplyr::recode_factor(sel$personalization,
"10 attention for party"="10",
"0 attention for candidate"="0")
sel$personalization <- as.numeric(as.character(sel$personalization))
sel$personalization <- (sel$personalization-10)*(-1)4.3 Logistic regression
We can conduct the logistic regression predicting the fact of hiring a consultant:
sel$party_list <- relevel(sel$party_list,"Other party")
model <- glm(consultant ~
personalization + party_list,
data=sel,
family = "binomial")
stargazer::stargazer(model, type="text",
single.row = T,
omit.stat = c("all")
)
=============================================
Dependent variable:
---------------------------
consultant
---------------------------------------------
personalization 0.204*** (0.030)
party_listCVP/PDC 0.438 (0.292)
party_listFDP/PLR 1.244*** (0.285)
party_listGLP/PVL -0.198 (0.393)
party_listGPS/PES 0.109 (0.361)
party_listSP/PS 0.796*** (0.289)
party_listSVP/UDC 0.496 (0.329)
Constant -3.654*** (0.244)
=============================================
=============================================
Note: *p<0.1; **p<0.05; ***p<0.014.4 Interpretation
Let’s interpret the regression output for the candidates from the SVP (right-wing party) and with a very personalized style of campaigning.
4.5 logit versus odds versus probability
- The logit is given by the model. It is equal to log(odds) = log(p/(1-p)). It cannot be interpreted further than its sign (direction of the effect).
- The odds indicates the direction and strength of the effect (no effect when =1, positive effect when >1, and negative effect when <1).
- In our example: for each 1 point increase on the personalization scale, the odds increase with a factor exp(0.20)=1.22=22%.
4.6 Model fit
The LogLikelihood measure (logLik function) is useful for comparing models after the addition of variables. In analogy with the linear regression, the pseudo-R2 can often be interpreted as part of the variance explained by the model.
5 Quiz
5.1 Can I answer these questions?
function quizInput({ questions, options}) {
let answers = questions.map(() => null);
let root = htl.html`<div
style="
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 10% 10% 70% 10%;"
>
${options.map(
(opt) => htl.html`<div style="font-weight: bold">${opt}</div>`
)}
<div style="font-weight: bold">Statements</div>
<div style="font-weight: bold"></div>
${Array.from(questions.entries(), ([i, [question, correct]]) =>
quizInputRow({
question,
options,
correct,
onChange: (newAnswer) => {
answers[i] = newAnswer;
root.value = answers;
root.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent("input"));
}
})
)}
</div>`;
root.value = answers;
return root;
}
function quizInputRow({
question,
options,
correct,
onChange = () => {}
}) {
let root = htl.html`<div>`;
function setAnswer(answer, initial = false) {
morph(
root,
htl.html`<div style="display: contents">
<form style="display: contents">
${options.map(
(opt) =>
htl.html`<label> </label>
<input
name=${question}  
type="radio"
value="${opt}"
checked=${opt === answer}
onChange=${() => setAnswer(opt)}
>
</input>`
)}
</form>
<div>${question}</div>
<div>   ${
answer === null ? "" : answer === correct ? "🟢" : "🔴"
}</div>
</div>`
);
root.value = answer;
if (!initial) {
root.dispatchEvent(new CustomEvent("input"));
onChange(answer);
}
}
setAnswer(null, true);
return root;
}
morph = require("https://bundle.run/nanomorph@5.4.2")True or false?
MC_1_1 = [
["The logit cannot be interpreted further than its sign", "true"],
["To transform log odds into probabilities, we use the following formula: exp(x)/(1+exp(x))", "true"],
["I can rely on the LogLikelihood measure to compare models after adding more explanatory variables", "true"],
["Odds ratio give us an indication about the magnitude of the implied change in the probabilities", "false"]
]
viewof answers_1_1 = quizInput({
questions: MC_1_1,
options: ["true", "false"]
})
Punkte_1_1 = {
const Sum =
(answers_1_1[0] == MC_1_1[0][1])*1 +
(answers_1_1[1] == MC_1_1[1][1])*1 +
(answers_1_1[2] == MC_1_1[2][1])*1 +
(answers_1_1[3] == MC_1_1[3][1])*1
var Punkte_1_1 = Sum - 2
if (Punkte_1_1 < 1) {Punkte_1_1 = 0}
return(Punkte_1_1)
}Score:

Multivariate statistics